ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
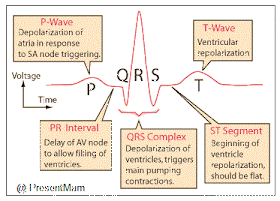
- Electrocardiogram is the recording of the electrical changes
that accompany the cardiac cycle.
- An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a test that checks for problems with the electrical activity of your heart. An EKG translates the heart's electrical activity into line tracings on paper. The spikes and dips in the line tracings are called waves
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a medical test that detects cardiac (heart) abnormalities by measuring the electrical activity generated by the heart
- Electrocardiogram is the instrument used to record potential
differences of heart muscles.
- A normal ECG consists of P wave, QRS wave & T-wave.
- The first wave, called P-wave is a small upward deflection &
represents atrial depolarization
- The Second wave, called QRS complex, begins as downward
deflection, continue as a large upright, triangular wave, and ends in a
downward wave.
- The QRS complex represents rapid ventricular depolarization.
- QRS complex is related to ventricular systole (Contraction)
- The third wave is dome-shaped upward deflection called
T-wave indicating ventricular repolarization.
- ECG is valuable in diagnosing
- a.
Abnormalities of conducting pathway
- b.
Enlargement of heart
- c.
Myocardial infraction
- d.
Electrolyte & hormonal imbalances.
- In reading an ECG, the size of the wave can provide
information about abnormalities
- Larger P waves indicate an enlargement of an atrium
- An enlargement Q wave may indicate a myocardial infraction
- An enlarged R wave
generally indicate enlarged ventricles
- The T wave is flatter than normal when the heart muscle is
receiving insufficient oxygen due to coronary heart disease
- The T Wave may be
elevated during high blood K+ level (hyperkalemia)
- The analysis of an ECG also involves measuring the time
spans between waves, which is called intervals or segments
- The P-Q intervals is the time from the beginning of the
P-Wave to the beginning of The QRS complex
- The P-Q interval is the time required for the action
potential to travel through the atria , AV node & rest of the conduction
system
- In Coronary heart disease & rheumatic fever, the P-Q
interval lengthens
- The S-T segments begins at the end of the S Wave and ends at
the beginning of the T-Wave.
- The S-T segments is the representations of the time between
the end of the spread of the impulse through ventricles & its repolarization.
- The S-T segmented is elevated in acute myocardial infraction
& depressed when heart muscle receives insufficient oxygen
- The Q-T interval extends from the start of QRS complex to
the end of the T wave

- The Q-T interval is the time from the beginning of ventricular
depolarization to the end of ventricular repolarizarion
- The Q-T interval may be lengthened by myocardial damage,
myocardial ischemia or conduction abnormalities
- You can Check ECG Stimulator Online = Here


No comments:
Post a Comment